LeongOrthopaedicHealth@gmail.com
This article is an aside to explain the physiology of weight training and why you only need to Weight Train Once a Week! Plus an explanation of how we came up with The Ten Principles of The WOW Method.
Note: at the bottom of this article is a glossary of terms.
The Physiology of Weight Training and Why Once a Week Works!
The principles of The WOW Method are not original. It started with Arthur Allen Jones, inventor of the Nautilus exercise machines. Jones developed the basic principles of High Intensity Training (HIT) as an alternative to Arnold Schwarzenegger’s ideal of hour upon hour of weight-lifting in the gym.
HIT advocates:
- Training to complete muscular exhaustion ensures you’ve exhausted all muscle fibres in a muscle group (see Henneman’s Size Principle).
- Exhausting all the muscle fibres in a muscle group ensures each fast-twitch fibre is stimulated to build new contractile units over the next week.
- New contractile units built into fast-twitch muscle fibres means bigger stronger muscles!
- Fast-twitch fibres need 6 to 7 days to recover completely. Training them more often interferes with the recovery process and causes inflammation.
- Progressive overload – as strength increases, the weight increases.
(Note: The following explanation of physiology has been greatly simplified out of respect for the layperson’s time.)

Different body-builders modified Jones’ HIT method in different ways. For instance, Ellington Darden believed in full-body workouts. Dorian Yates split his workouts into four sessions a week. Mike Mentzer advocated in his book, High Intensity Training the Mike Mentzer Way, one set per muscle group until muscular failure and then rest for 4 -7 days. Dr. Doug McGuff recommends in his book, Body By Science, 5 different exercises using HIT with super-slow reps for 90 seconds each.
Case-in-point: if bodybuilders can achieve their ideal form by weight training once per week, then doesn’t it stand to reason that you’ll be able to make significant gains using the same method?
Wait. I Don’t Want to be a Bodybuilder!
Most don’t want to be that weird muscle-bound gym person. We get it! We aren’t weird muscle-bound gym people either.
Most bodybuilders are successful because they possess the correct genetics — a mesomorphic body type. Then they have the desire and will to become bodybuilders.
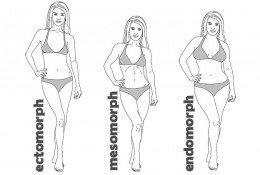
- Ectomorphic: long, thin muscle. Not predisposed to store fat or build muscle.
- Mesomorphic: large bones, above average muscle mass. Predisposed to build muscle.
- Endomorphic: medium bone structure, wide hips. Predisposed to store fat.
Rarely will a man or woman grow more muscle mass than they want. If you’re mesomorphic and start to become “too big”, then weight train every two weeks … or even once a month.
The main goal is to prevent Sarcopenia and preserve your muscle mass as you grow older.
The Importance of Weight Training
Burn fat like you did years ago.
Consider this: a slow metabolism can sustain a bear through months of hibernation without eating. Speed up your metabolism!
Muscles need food.
Between 25 to 35 years old, you start to lose half-a-pound of muscle per year. Lost muscle fibres can never be re-gained! When you lose muscle, the amount of calories your body uses decreases too. That’s why people seem to replace muscle with fat as they age.
Use it or lose it.
Weight train and you strengthen and keep most of your muscle mass. This boosts your metabolism for as long as you have that muscle density — even while sleeping!

Another perk: increased muscle mass helps the body manage blood-sugar levels. Meaning, you can get away with a little more sugar (or alcohol, bread, potatoes, pasta) before your body converts it to fat.
EVERYONE needs to weight train with correct form, impeccable posture, and an effective amount of weight. (Although for some people a physician’s clearance may be necessary.)
Why Wait Seven Days Before Training Again?
Dr. Doug McGuff states that the average muscle-recovery time for the general population is seven days.
Building new tissues within the body happens at a set rate — usually a full seven days to:
- Allow the fatigue and inflammation to dissipate
- Repair tears in the muscle fibres
- Build new contractile units within the muscle fibres
- Strengthen the tendons, ligaments, fascia, and bones so that they are strong enough to support the stronger muscles
Does seven days seem like a long time? Rest assured, you will not lose muscle in that time (unless you lack nutrients).
Why Only One Set per Muscle Group?

Dr. Doug McGuff states that multiple weight-training sets are akin to pressing the elevator button repeatedly (when the first press of the elevator button already called the elevator car).
Ditto! One set is all it takes to stimulate the building of new contractile units within the muscle fibre. Further sets increase fatigue and inflammation. Energy your body could be using to build new contractile units.
How Heavy Should I Lift?
Dr. Doug McGuff explains in his book, Body by Science, that light weights are ineffective. Slow-twitch fibres are recruited first. But because they fatigue slowly, by the time the fast twitch fibres are triggered, the slow-twitch motor units have recovered and are cycling back to the contraction process, preventing the fast-twitch fibres from being further engaged.
There’s a similar problem with too-heavy weights allowing too few repetitions. Both the fast motor units and slow motor units are engaged, but the fast-twitch units fatigue so quickly that the muscle will fail before all the slow twitch fibres are properly stimulated.
Dr. McGuff argues that a moderately-heavy weight allows full recruitment and stimulation of all muscle fibres before muscle failure.
Am I Too Old to Weight Train?

It’s never too late to start! Anyone 14 years old and up will reap staggering results from weight training. (Although a doctor’s medical clearance might be necessary.)
Many elderly men and women stay healthy through weight training. Clarence Bass, born in 1937, is one such gentleman. He’s the author of a fitness blog and many books including, Take Charge: Fitness at the Edge of Science.
As per the scientific literature, Strength and Endurance Training Prescription in Healthy and Frail Elderly: “… it seems that exercise interventions that include endurance, strength, and muscle power training should be prescribed to frail elderly in order to improve the functional capacity.”
As per the study, High-Intensity Strength Training in Nonagenarians, Effects on Skeletal Muscle: “A high-intensity weight-training program is capable dramatic increases in muscle strength in frail men and women aged in their 90s, in spite of their advanced age, extremely sedentary habits, multiple chronic diseases, functional disabilities, and nutritional inadequacies.”
LEONG Orthopaedic Health’s observations:
- Low-to-moderate resistance training produces little increase in strength in older adults.
- Strength gains are first due to improved neural-recruitment patterns and hypertrophy comes later.
- Healthy happy independent living requires strength, flexibility, and functional movements.
The Physiology of Weight Training Glossary
- Accessory muscles are the stabilizing and assisting muscles that sometimes get left behind with ongoing weight-training (Infraspinatus, Serratus Anterior, Gluteus Medius).
- Fast-Twitch Motor Unit is comprised of a nerve and many fast-twitch muscle fibres. These fast-twitch fibres fire rapidly and fatigue quickly.
- Ligaments are the fascial tissue connecting bones, thereby stabilizing a joint.
- Prime Mover Muscles are the primary muscles moving body parts (quadriceps during squats, latissimus dorsi in lat pulldowns, and triceps brachii during close-grip bench press).
- Repetition (rep) is the controlled lifting and lowering of the weight through the full range of motion.
- Temporary Muscular Failure means performing repetitions until momentary muscular failure where, although you are engaged in lifting the weight (eg. bicep curl), the arm doesn’t move because all motor units are exhausted. Note: It is not absolutely necessary to lift to complete muscular failure, it’s just the most efficient way to gain strength and size.
- Set consists of several repetitions without rest.
- Slow-Twitch Motor Unit is comprised of a nerve and many slow-twitch muscle fibres. These fibres fire slowly and can maintain continuous muscle contractions over extended periods.
- Tendons are the fascial tissue connecting muscle to bone.
Sources
Evidence-based research has become so de rigueur every theory is expected to be based upon it. However, we can’t help but notice that with just a bit of research on Google, any theory can easily be either proven or disproven.
Both above and below we’ve included several studies, or articles based upon studies. However, The WOW Method (created by LEONG Orthopaedic Health) is mostly based upon the last thirty years of results with our clientele.
- Strength Training Methods and the Work of Arthur Jones
- Strength Training for Health and Longevity with Doug McGuff, MD
- Comparison of once‐weekly and twice‐weekly strength training in older adults
- Recovery after heavy resistance exercise
– LEONG Orthopaedic Health
Ready to transform your body with one full-body weight-training session a week? Contact us today:
personal training
by appointment only. Please email:
LeongOrthopaedicHealth@gmail.com
If you like this article, please share it!
All rights reserved; no part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying or otherwise, without prior permission. Copyright 2015.
